ultrasound imaging and color Doppler ultrasound imaging?
About 20 years ago, some pioneers who were committed to introducing foreign ultrasound training systems, especially those from the United States, obtained a batch of North American ultrasound job examination questions through various channels. One short answer question asked: What's the difference between COLOR ULTRASONOGRAPHY and COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASONOGRAPHY?
What is the difference between color ultrasound imaging and color Doppler ultrasound imaging?
As soon as color Doppler ultrasound imaging entered China, it was referred to as "color ultrasound". Chinese ultrasound doctors have always equated color ultrasound with color Doppler ultrasound, so China saw this problem for the first time. The doctors looked confused and didn't know what the question was asking.
Actually, this is a very simple question.
Color ultrasound refers to displaying a specific signal of echo information during ultrasound examination with special color coding rules, which is color ultrasound imaging. These specific echo information can be echo intensity, Doppler frequency shift, hardness information, microbubble information, etc.
so. Color Doppler imaging is only one of many color imaging modes. It extracts the Doppler frequency shift information from the echo information and displays it in the form of color coding.
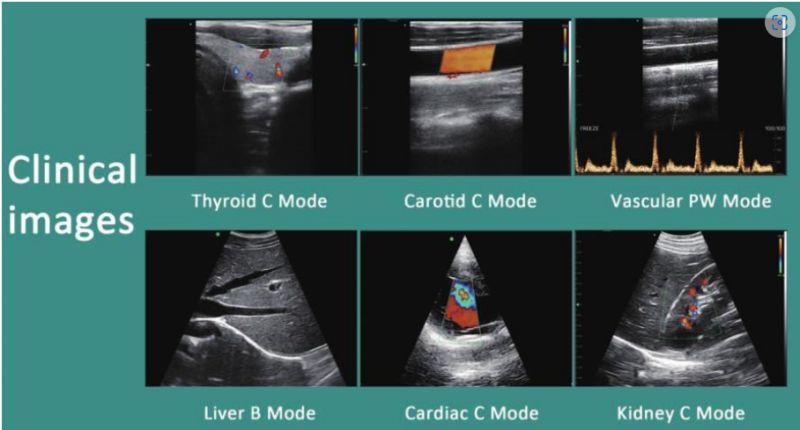
In addition to the color Doppler imaging that we are familiar with, let’s take a look at the color ultrasound imaging modes.
We know that two-dimensional gray-scale ultrasound displays the intensity of the echo signal in the form of brightness encoding. If we color-code a certain area or all of the brightness, we will get a color-coded image.
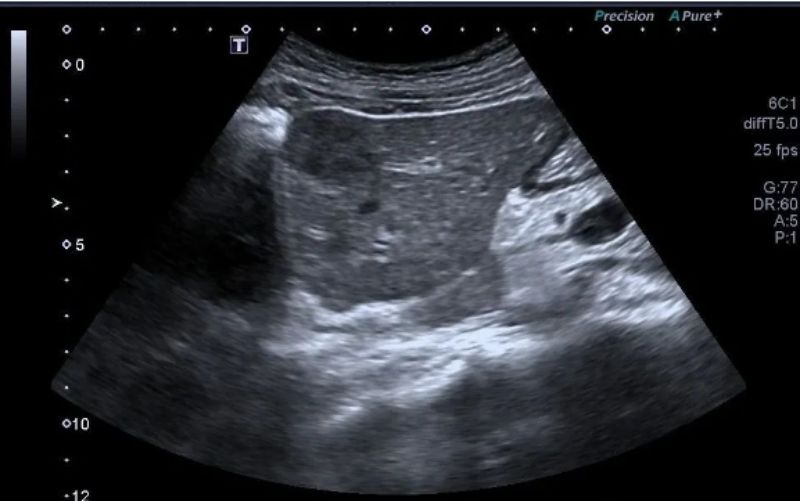
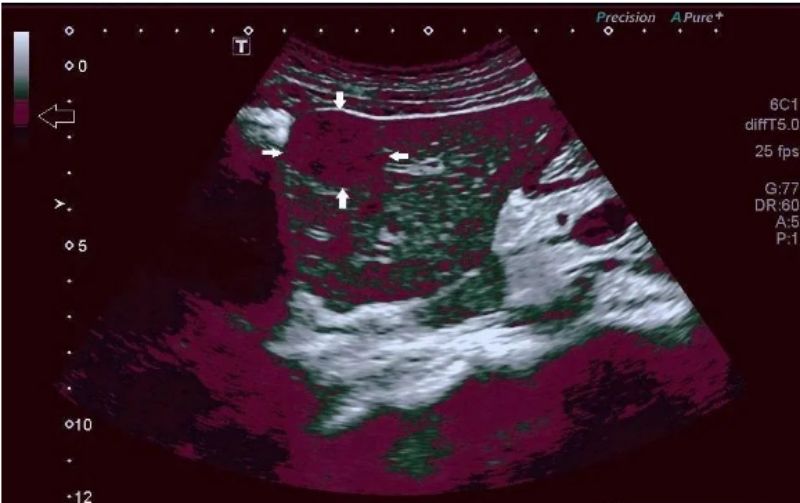
Above: A specific area in the grayscale signal is encoded in purple (open arrow), and the lesion with corresponding brightness turns purple (shown by solid arrow).
The above imaging method that encodes echo intensity in color or different color levels was very popular in China for a period of time in the early 1990s. It was called "2D pseudo-color imaging" at that time. Although many papers were published at that time, in fact The application value is very limited. At that time, many hospitals even used this image to pass off as color Doppler imaging to charge patients "color ultrasound fees". It was really shameless.
In fact, all color signals on color ultrasound imaging are pseudo-colors, and these color signals are artificially coded and set by us.
Most manufacturers of ultrasonic elastography , which is currently very popular, also display the hardness (or elastic modulus) of tissue or lesions in a color-coded form, so it is also a type of color ultrasound.

Above: Shear wave elastography shows the elastic modulus of the lesion in color scale coding.
When a small amount of microbubbles explode, a strong nonlinear effect will be produced, which is often not positively correlated with the echo intensity. We call this mode of extracting non-correlated information for imaging non-correlated imaging. Non-correlation imaging is mainly used to display very small amounts of microbubbles and is very useful in microbubble-targeted ultrasound research. Typically, this non-correlation is also displayed in a color-coded form, so it is also a color imaging.
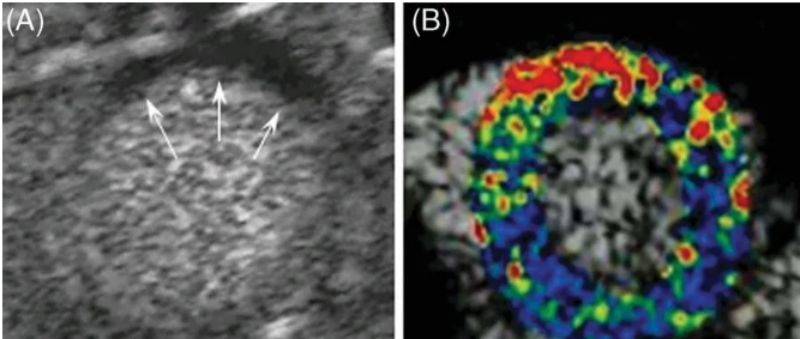
Above: p-selectin microbubble-targeted imaging shows selective enhancement of the anterior wall after ischemia, and myocardial contrast-enhanced sonographic cardiac short-axis images in left anterior descending ischemia-reperfusion in mice.
(A) Myocardial contrast-enhanced ultrasound shows an anterior perfusion defect (arrow) during myocardial ischemia.
(B) After 45 minutes of reperfusion. The color scale represents the intensity of non-correlated imaging of targeted microbubbles.
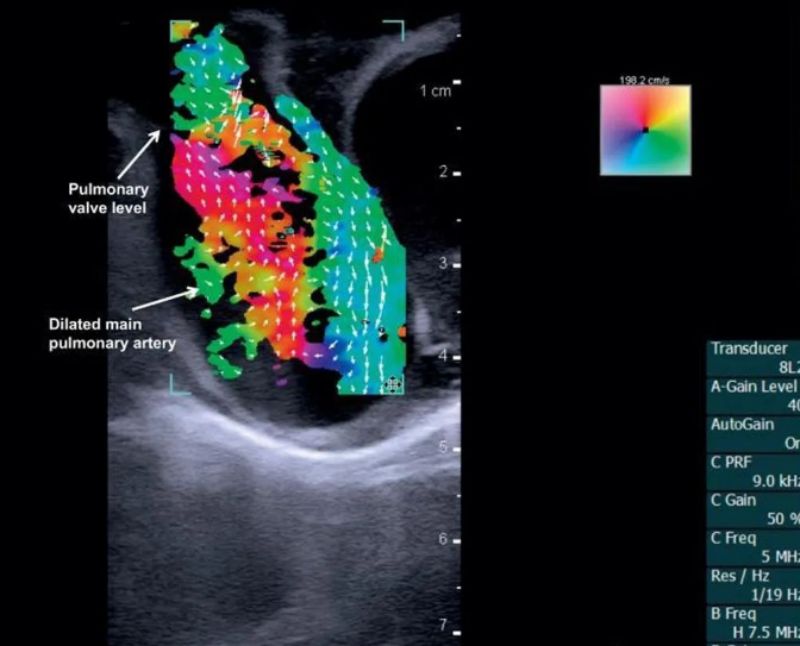
The blood flow vector imaging below is also a color ultrasound imaging mode
Post time: Nov-11-2023